How Does One-Time Password Hijacking Work?
For years, Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) has been touted as the gold standard of account security. The logic is simple: even if a hacker steals your password, they can't get in without that second piece of evidence—the One-Time Password (OTP). However, the "Utility-to-Security Bridge" has a major flaw here. The most common 2FA methods, like SMS and email codes, are popular because they are incredibly convenient, not because they are the most secure.
In fact, the very features that make OTPs easy to use—universal access via your phone or inbox—are the same features hackers exploit to hijack accounts. Understanding how this "convenience tax" works is the first step toward building a truly resilient workflow.
Looking for a way to manage team access without the 2FA headache? TeamPassword provides a secure, encrypted platform to share logins without relying on vulnerable SMS shortcuts. Get started with a 14-day free trial.
Table of Contents
What is OTP Hijacking?
A One-Time Password is a short-lived code sent to a user to verify their identity. While it feels secure, OTP hijacking occurs when an attacker intercepts this code before you can use it—or trick you into giving it to them. Because many services use these codes not just for login, but for password resets, a hijacked OTP often results in total account loss.
The 3 Ways Your Codes are Compromised
1. SMS Interception (The Network Flaw)
SMS was never designed for security; it was designed for communication. Methods like SIM Swapping involve a hacker tricking a mobile carrier into porting your phone number to their device. Once they control your number, they receive every 2FA code intended for you. More sophisticated attackers exploit the SS7 protocol—the backbone of global cellular networks—to "sniff" messages out of the air without ever touching your phone.
2. The "Notification Peep" (The Physical Flaw)
Utility dictates that we want to see our messages quickly. By default, most smartphones display a preview of incoming texts on the lock screen. A bad actor in a physical space—like a coffee shop or office—can harvest your OTP without needing to unlock your device or install malware.
3. Social Engineering Bots (The Human Flaw)
This is the most modern threat. An automated bot calls you, pretending to be your bank or a service like PayPal. It claims there is "suspicious activity" and asks you to "verify your identity" by typing the code you just received into your keypad. In reality, the bot triggered a login attempt, and you are handing the hacker the final key they need in real-time.
How to Prevent Hijacking: A Priority Checklist
Security fatigue is real. If you try to do everything at once, you’ll likely do nothing. Here is how to prioritize your defenses, moving from critical infrastructure changes to daily habit adjustments.
Tier 1: The "Must-Haves" (Critical Infrastructure)
These changes provide the highest level of protection with the least amount of daily effort once configured.
- Switch to Authenticator Apps: Move away from SMS-based 2FA. Apps like Google Authenticator or Ente Auth generate codes locally on your device, meaning they cannot be intercepted via SIM swapping or SS7 attacks.
- Use a Dedicated Password Manager: Using a tool like TeamPassword ensures that your primary passwords are randomly generated and encrypted. This prevents the initial "password leak" that leads hackers to trigger an OTP request in the first place.
- Hardware Keys (U2F): For your most sensitive accounts (like primary business email), use a physical security key. It is currently the only 2FA method that is virtually immune to phishing.
Tier 2: System Hardening (The "Convenience" Tweaks)
These settings close the "hidden" doors that hackers use for physical or social attacks.
- Hide Lock Screen Previews: Change your phone settings so that notification content is only visible after the phone is unlocked. This stops "over-the-shoulder" OTP theft.
- SIM PIN Protection: Add a PIN to your SIM card itself. Even if a thief steals your physical SIM card, they won't be able to use it in another phone to receive your texts.
- Audit Recovery Methods: Remove your phone number as a "recovery option" on sensitive accounts. Hackers often use the "Forgot Password via SMS" feature as their primary entry point.
Tier 3: Behavioral Awareness (Daily Habits)
Technology can only go so far; your team's habits are the final line of defense.
Always type your OTP directly into the browser or app you are logging into. Never relay a code over a phone call, text message, or email. Reliable services will never ask you to "confirm" a code via a voice prompt or a reply-text. Additionally, ensure you are updating your OS and browser regularly to patch the vulnerabilities that MITM attacks exploit.
The Evolution of Authentication
Using any form of 2FA is significantly better than using none at all. However, as hackers move from targeting "data" to targeting "workflows," your security strategy must evolve. By shifting from SMS to app-based or hardware-based authentication, you remove the largest vulnerabilities from your team's daily routine.
TeamPassword is built to help teams stay fast without staying vulnerable. By centralizing your logins in a secure, encrypted vault, you eliminate the "convenience traps" that lead to breaches.
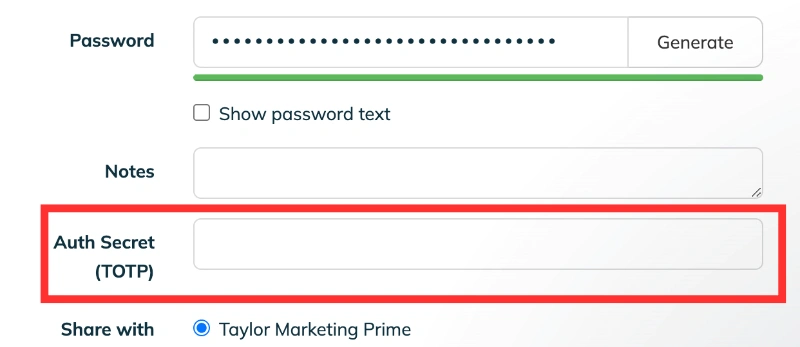
TeamPassword includes a built in TOTP secret generator, meaning that your time-based one-time codes are generated right within the vault.
Try TeamPassword for free for 14 days and simplify your security workflow today.